National Agricultural Meteorology Monthly
Summary of this month
Most of the country's agricultural areas have high temperatures, only in the central and eastern parts of Inner Mongolia, the southwestern part of northeastern China, and the southwestern part of the country, which is 1~2°C lower; the eastern part of the northwestern part, the southern part of North China, the Huanghuai, Jianghuai and Jianghan are obviously less precipitation, and the middle and east of the south of the Yangtze River. There are more than one in the western and western parts of South China and the south and southwest of southwest China. In the northeastern part of the country, there were more precipitation and lower temperatures in mid-June, and some rice crops were affected in the first season. The wheat harvesting area in the north is sunny and fine, and the wheat harvest is progressing smoothly; the summer sowing area has a wide range of drought, and the crop growth and summer planting process are affected. In most parts of the south, heavy precipitation weather is frequent, and floods occur locally; in the southwestern part of the country, there are more rainy days in the first half of the year, which is not conducive to the summer harvesting work.
Weather and climate characteristics this month
Most of the country's agricultural areas are 1 to 2 °C higher, and the central and eastern parts of Inner Mongolia, the southwestern part of Northeast China, and the southwestern part of the country are 1 to 2 °C lower (Fig. 1). The precipitation in the eastern part of the northwest, southern part of North China, Huanghuai, Jianghuai and Jianghan is less than 50% to 10%; the central and eastern parts of the south of the Yangtze River, the western and northern parts of South China, and the south and southwestern parts of the southwest are more than one to two times (Fig. 2). The number of precipitation days in the northeastern region and the south is 15 to 20 days, and in some areas it is 20 to 30 days (Figure 3). Inner Mongolia, Northwest China, and Huanghuai have more sunshine, and most of the other agricultural areas have less sunshine. The southern part of the country has less than 100 hours of sunshine per day and less than 50 hours to the east of the southwest (Figure 4). 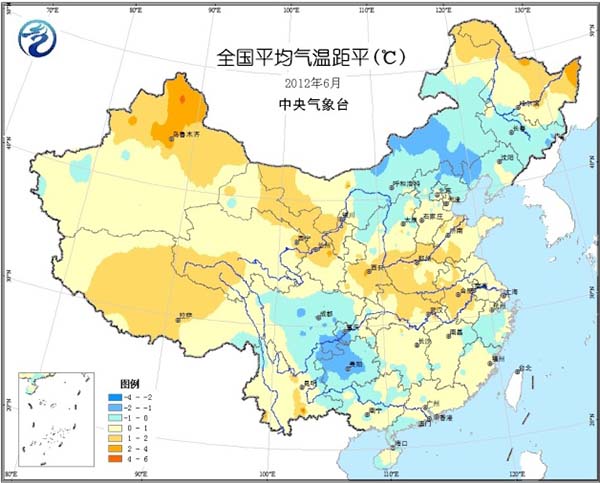
Figure 1 Average temperature anomaly in June 2012 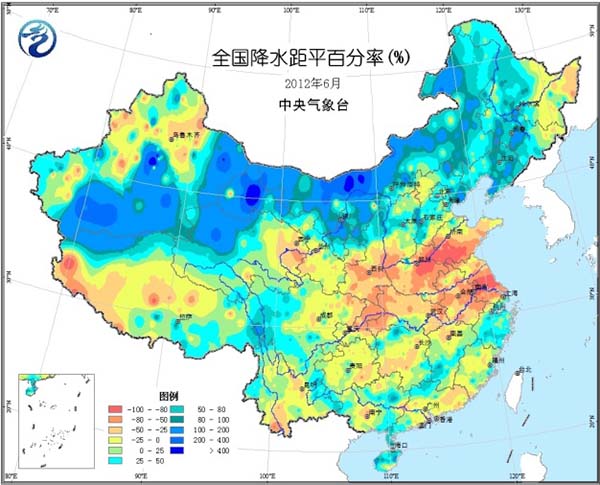
Figure 2 Percentage of precipitation anomalies in June 2012 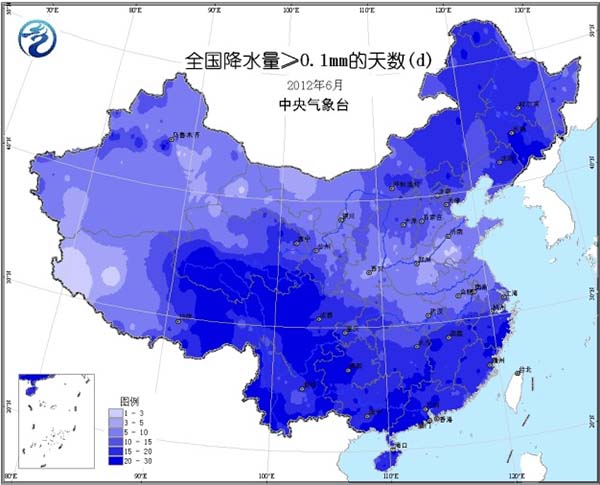
Figure 3 Precipitation days in June 2012 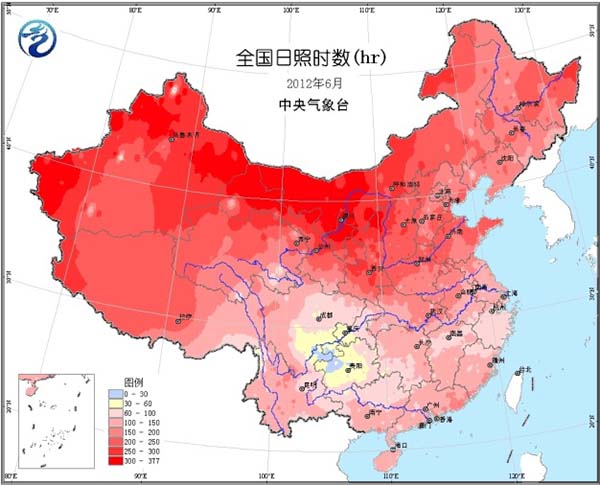
Figure 4 Sunshine hours in June 2012
Analysis of agricultural meteorological conditions in major agricultural areas this month
Inner Mongolia and Northeast China: The precipitation in the month is more than 50% to 2 times. The temperature in the central and eastern Inner Mongolia and the southeastern part of the country is 1-2°C lower. Especially in the eastern part of the eastern region, there are more precipitations and lower temperatures, and there are obvious low temperature periods. Among them, the eastern rice area of ​​Jilin Province has a low temperature of 5 to 10 days with an average daily temperature of ≤ 15 °C, and some of the rice tillers in the first season stop, affecting effective tillering. In the second half of the year, the precipitation in the northeast region changed from a little to a small, and the temperature changed from a low to a high, which is conducive to make up for the adverse effects of the early low temperature on the crop.
Northwest, North China, Huanghuai: The northern wheat harvest area has fine weather, most of the rain days are less than 5 days, and the main precipitation is favorable for wheat harvesting, and the winter wheat harvest is progressing smoothly. Since May, precipitation in southern China, most of Huanghuai, northern Jianghuai, northern Jianghan and other places is significantly less than normal. The precipitation this month is less than 10 mm. In high temperature weather, the number of high temperature days in some areas reached more than 12 days, which made the drought in summer sowing area develop rapidly. The summer planting crops were deficient in seedling and ridge. The rice in one season could not be planted in time, and the summer planting process was affected. At the end of the month, Huanghuai and Jianghuai experienced significant precipitation, and the agricultural drought was alleviated, and the scope was significantly reduced.
Jiangnan and South China: The number of rainy days in the month is 15 to 20 days. There are many heavy precipitations. In some areas, there are 3 to 5 days of heavy rain. The accumulated rainfall is 350-500 mm, which is not conducive to early rice flowering and pollination. Land floods and disasters, agricultural production suffered losses. Rainy and high humidity weather has led to rapid development of pests and diseases.
Southwest: During the month, there is more precipitation, and the drought is further alleviated, which is also conducive to the storage of water in the pond. However, local rainstorms have caused floods in farmland and agricultural production has suffered some losses. There are many rainy days. The precipitation days in some areas are 20 to 30 days, and the light is less than 100 hours. The growth and development of spring maize and rice are adversely affected. At the same time, the air humidity is high and the temperature is suitable to cause the spread of pests and diseases. In addition, in the first half of June, there were more rainy days in the eastern part of the southwestern region, and the illumination was less, which was unfavorable for the summer harvesting work.
Major agricultural meteorological disasters this month
The national agrometeorological disasters are mainly drought, heavy rain, hail, hail and crop pests.
Drought: During the month, drought occurred in parts of Gansu Gandong, eastern Ningxia, southeastern Shaanxi, southeastern Shanxi, central Shandong and southern peninsula, western Henan, northern Anhui, northern Hubei, etc. It is more than 10% slower than last year.
Heavy rains and floods: strong rainfall occurred in the eastern part of Inner Mongolia, most of the northeastern part of China, the south of the Yangtze River and the southwestern part of South China, and the southwestern part of the southwestern part of the country. Floods occurred in some areas, rice, corn, flue-cured tobacco, soybeans, sugar cane and other crops and fruit trees and vegetables. Both aquaculture suffered certain losses. According to incomplete statistics from the agricultural sector, as of June 24, floods caused an area of ​​30.72 thousand hectares affected by crops in Guangxi, including 10.14 thousand hectares of land and 1.8 thousand hectares. Affected by the tropical storm "Terry" No. 5 of 2012 and the No. 6 strong tropical storm "Du Suyu" (landing on the coast of Guangdong at 2 am on June 30), there were heavy storms and rains on the coast of South China, crops, fruit trees and vegetables. Agricultural facilities suffered some losses.
Gale, hail: In the month, the provinces with heavy wind and flood disasters include Xinjiang, Gansu, Inner Mongolia, Heilongjiang, Liaoning, and Shandong. Among them, on June 2, a hailstorm occurred in Heilongjiang Tieli, and the affected area of ​​crops (rice, corn, soybean) was 16 thousand hectares, with a disaster of 8.1 thousand hectares and a total of 4.2 thousand hectares.
Chilling damage: In the middle and southeast of the northeastern part of the country, there is a relatively obvious low temperature period. In the eastern part of Jilin Province, there is a low temperature of 5 to 10 days with an average daily temperature of ≤15 °C. Some of the rice tillers in the first season stop, which affects effective tillering.
Pests and diseases: During the month, winter wheat in some parts of southern Huanghuai developed scab, and rust occurred in parts of northwestern China; cotton was found in parts of Xinjiang, and cotton bollworms occurred in southern part of North China. Rice planthoppers occur in some rice in Chongqing, and some insect pests occur in Sichuan. Tobacco leaves in some areas of Yunnan suffer from leaf spot disease. 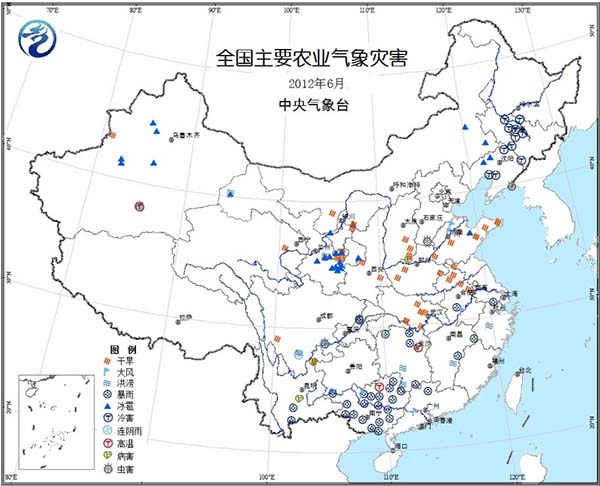
Figure 5 Agricultural meteorological disasters in June 2012
Outlook and recommendations for agricultural meteorological conditions this month
In July, spring-sown crops across the country will gradually enter the key stage of yield formation. Early rice is in the mature stage of grain filling. The crops of rice, corn, cotton, soybean and other crops are in a critical period of vegetative growth to reproductive growth, and late rice enters the planting stage. Midsummer is a season of strong convective weather, and all localities enter the main flood season. The coastal tropical cyclone activity will also increase significantly. Gale, hail, heavy rain and flood disasters will affect agricultural production.
It is expected that in July, the temperature in the western part of the northeastern region will be high and the precipitation will be less. In some areas, the soil over-wet condition will be improved, and it will also help to compensate for the adverse effects of the early rain and low temperature on the crop. Most of the North China and Huanghuai areas have more precipitation, and the drought is expected to be lifted, which is conducive to the growth and development of various crops. However, local precipitation in some areas may cause flooding or flooding in farmland.
The temperatures in Jianghan, Jianghuai, Jiangnan and eastern China are flat or slightly higher, which is conducive to crop growth. However, precipitation in the central and eastern parts of the Yangtze River is obviously less, and high temperature and drought may occur. It is necessary to do a good job in agricultural production water storage to prevent high temperature and heat damage. Drought and other adverse effects on crop growth and development. The temperature in the western and southwestern parts of South China is slightly lower and the precipitation is higher, which is conducive to the storage of water in the pond, but it is not conducive to the prevention and control of pests and diseases. Suggest:
The northeast region should timely cultivate and plan, and fertilize rationally to promote the healthy growth of crops. The eastern part should pay attention to clearing the ditch in time to prevent the occurrence of waterlogging; the western part should pay attention to water conservation and water storage to prevent drought.
In areas such as North China, Huanghuai and Northwest China that have completed summer sowing, it is necessary to promptly check seedlings and replant seedlings, and to plant seedlings. The areas that have not yet been planted should speed up the summer sowing schedule to avoid delays in farming. At the same time, it is necessary to timely cultivate and weed, clear the ditch, remove the sputum, reduce the waterlogging, rational fertilization, and promote the robust growth and yield formation of cotton, corn, soybean and other crops.
All parts of the South should do a good job in agricultural production water storage to reduce the risk of high temperature and drought. The early rice production area should be tempered by water to prevent the high temperature ripening hazard during the mature stage of grain filling, and promote the full grain filling of early rice and increase the grain weight. In the late rice planting area, it is necessary to timely carry out the management and land preparation work of the late rice paddy field, and plant it in time to avoid high temperature burns.
July is a season of typhoon, heavy rain, strong winds and hail. The localities have entered the main flood season. The weather forecast and disaster warning information should be closely monitored to prevent floods and floods. At the same time, due to the uneven distribution of precipitation, high temperature may lead to agricultural drought. Occurred, all localities should also strengthen water conservation and water storage, and do a good job in drought prevention and drought relief. In addition, the prevention and control of pests and diseases should be strengthened.
Foshan City, Nanhai District Huidexing Stainless Steel Products LTD., , https://www.huidexing.net