Control of welding quality and deformation of container ship thick plate
2023-09-21 15:09:35
The 18 000-container container ship that our company undertakes is currently the largest container ship built in China with a total length of 399.2m and a steel injection capacity of about 48,000 tons. The construction of the container ship, while breaking the monopoly of foreign companies in this field, also poses new challenges to the existing production process. Torsion box thick plate welding is one of them.
The maximum thickness of the container ship's torsion box slab has reached 85m, while the J U2000E series rigs currently built in the straight center are only 51m thick, so the welding of the torsion box slab is on site. It is a new challenge, and the existing thick plate welding process cannot meet the construction requirements of existing thick plates. In addition, because the existing thick plate has stricter requirements on precision and internal quality, this paper combs the production process of 18 000T EU torsion box thick plate, and introduces the welding process of the torsion box thick plate in detail.
1. Analysis of the performance of steel
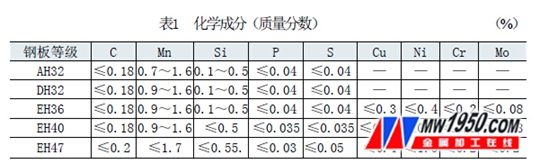
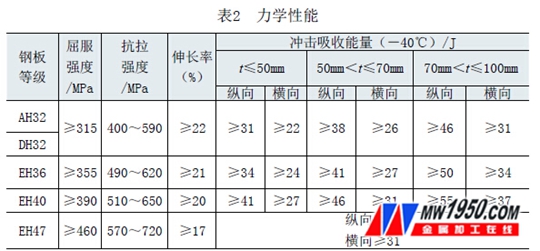
EH grade high-strength steel is a commonly used steel plate in the shipbuilding process. In addition to high strength and good plasticity, it also has good toughness, so it has been widely used in marine steel plates. EH grade high strength steel can meet the impact performance requirements at -40 ° C low temperature operation. The chemical composition of the EH grade steel sheet and the mechanical properties at -40 ° C are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
2. Welding process
Due to the large tendency of thick plate welding cracks, the occurrence of welding cracks will seriously affect the welding quality and production rhythm, and may also bring catastrophic accidents. Therefore, the selection of welding and preheating processes is very important. The welding process.
(1) Selection of welding methods At present, there are mature and high-efficiency welding types in the straight working area: FCB welding, submerged arc welding and CO 2 welding. FCB welding can form the steel plate below 38m in one time. The thickness of the outer side of the torsion box has far exceeded the FCB welding capacity, so the possibility of FCB welding is excluded. At the same time, considering the large workload of super-thick plate welding, high working intensity and many deposited metal, combined with the existing welding process and the successful experience of J U2000E thick plate welding, monofilament submerged arc welding becomes thick plate welding. Preferred.
(2) Selection of welding materials In order to meet the strength requirements of the torsion box welds, the selection of welding consumables in the submerged arc welding is A 5 Y 4 6 M, while meeting the AWS welding grade A5.23: EN I2 It is required that the welding material be selected and used according to the process requirements and the base metal. The specific selection is shown in Table 3.

3. Points of attention in the welding process
(1) Before cleaning, the welding area must be cleaned before welding, and the water, oil, cutting slag, oxide and rust in the range of 20m on both sides of the welding groove should be removed, and the welding impurities can be reduced while reducing The source of hydrogen during the welding process.
(2) Positioning welding Positioning welding adopts CO 2 semi-automatic welding, welding material selects GFR-81K2, preheating requirement is consistent with preheating temperature requirement of formal weld, preheating by oxyacetylene flame, positioning welding length ≥100m m, height ≤6m m, the spacing of the tack welding is about 500m, and cracks, pores and slag inclusions are not allowed in the tack welding.
(3) The selection of the arc-guiding plate and the lead-out plate is an ultra-thick plate. The selection of the arc-striking plate and the lead-out plate will directly affect the quality of the joint end. In the super-thick plate welding process, the arc-starting plate The lead plate cannot be simply selected for assembly. The groove shape should be consistent with the shape of the base material groove. The plate thickness difference between the arc runner plate, the lead plate and the weldment should be controlled within ±2 mm.
(4) Preparation of groove The shape of the groove and the angle of the groove have a direct influence on the amount of weld metal and the crystallization process. The shape of the groove on the site is mainly X-shaped, 50° on the upslope and 70° on the lower slope. The depth of the upslope and the root of the weld are 2/5 of the thickness of the weld. In the actual welding process, the welding deformation tends to the frame surface with a large amount of welding, and at the same time, the excessive rooting causes the workload of turning over the carbon planing to be greatly increased. In order to reduce the amount of welding deformation and the carbon shaving loss after turning over, the site is welded according to the actual situation. The groove has been improved, and the comparison of the front and back forms is shown in Figure 1. When the groove angle is reduced, the thickness of the residual root is reduced, and the filler metal of the main weld is reduced, which not only reduces the loss of the welding consumables, but also greatly reduces the workload of the carbon planing after turning over, and can be turned over after 3 times of improvement. Finishing the 85mm thick steel plate.
(5) Preheating process The preheating requirements for steel plates of different materials and thicknesses are shown in Table 4.
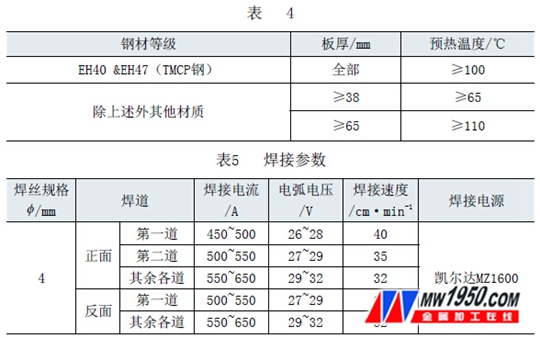
(6) Welding parameters Two key points of thick plate submerged arc welding are internal quality and welding deformation. Properly increasing the preheating temperature and appropriately increasing the heat input can reduce the deformation and reduce the tendency of crystal cracking. The welding parameters of the 85m m thick plate are shown in Table 5.
Due to the large thickness of the steel plate and strong rigidity constraints, in order to avoid the occurrence of solidification cracks and the residual root penetration, the first two front and the first side of the reverse side should be welded by a small current rapid welding method.
(7) Thick plate deformation control For the 8 5 mm thick plate butt joint, the following welding sequence is used in actual production: the first to the 10th weld bead is welded on the front side, the back is replaced with the carbon arc gouging on the back, and the back is finished. Solder 11~22, then flip, weld 23~48, and finally turn over and weld 49~62. During the welding process, it is necessary to pay attention to the heating and heating of the weld before and after turning over, and keep the temperature >100 °C. During the welding process, 10t pressure iron should be placed on both sides of the plate to reduce the upturn deformation during the welding process.

figure 1
The specific process is as follows:
First, the structural surface is subjected to CO 2 manual arc welding for positioning. The positioning welding standard refers to the above-mentioned tack welding process. After the positioning is completed, the welding slag is cleaned, and then the submerged arc welding operation is performed on the first to the tenth, and the first pass adopts the small current rapid welding. The method of welding, the welding number of each channel is shown in Table 5. After the welding, the height of the plate to the structural plane is H=20~24mm (see Figure 2).
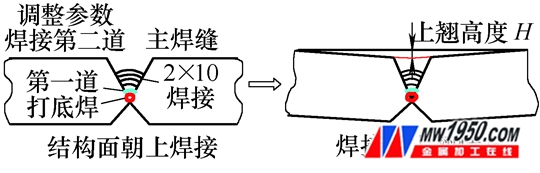
Figure 2 welding before turning over
Secondly, the first turn over is to cut the root of the unstructured groove. After the treatment, the root of the groove becomes U-shaped, the depth is 28 ~ 3 3 mm, and the deformation H1 after carbon planing is around 3 ~ 5 mm. After the polishing, the non-frame surface is welded 11~22 times. After the welding, the height of the plate to the non-structural surface is H2=15~20mm (see Figure 3).
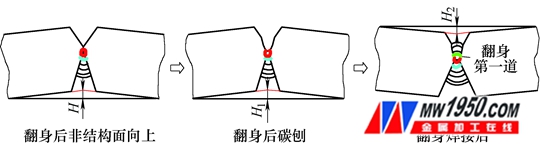
Figure 3: Welding after the first turn over
Thirdly, the second time, the submerged arc welding of 23~48 channels is performed on the structural surface. After the welding is finished, the height H3 of the plate to the structural plane is 25~30 mm (see Fig. 4).
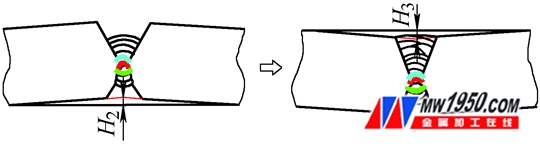
Figure 4 welding after the second turn
Fourth, the third turn over the 49-62 welding of the non-structural surface, the plate is in an arch state after the welding, and there is basically no welding deformation (see Figure 5).
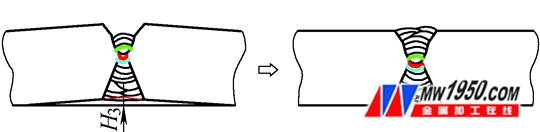
Figure 5: Welding after the third turn
Immediately after welding, the insulation is covered with heat-insulating cotton, and the post-weld slow-cooling heat treatment is performed to prevent the formation of hardened structure to meet the mechanical properties of the welded joint. Field practice proves that the above welding process can meet the quality and precision requirements of the torsion box thick plate welding, and can guide the subsequent thick plate welding.
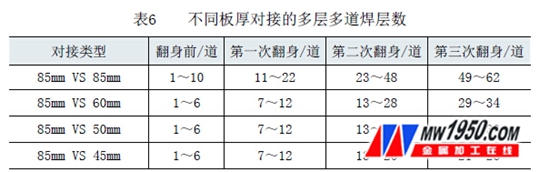
The above is the statistics of the number of welded layers for the 8 5 mm thick plate. The number of layers of the multi-layer multi-pass welding when the different thicknesses are docked is shown in Table 6.
(8) Rework and surface treatment of welding defects The weld repair is carried out by C O2 welding, and the welding grade should be the same as that required by the original welding head. When welding, the weld repair should be preheated to above 100 °C, and the weld length of the local repair must be >50 mm.
4. Flaw detection requirements
The detection of the torsion box thick plate is more strict than the previous flaw detection. The traditional flaw detection performs single-sided and double-sided UT detection on one side of the weld, and the UT detection of the torsion box thick plate is 100% inspection of the weld on both sides, effectively avoiding the miss detection of the weld defect, and at the same time detecting the defect. More sensitive. Ultrasonic testing of on-site slabs must be carried out within 48 hours after welding.
5 Conclusion
18 000T EU is our company's difficulties in serving in recent years. It lasted for 6 months and successfully completed 172 sets of ultra-thick plate welding of container ships. The pass rate of ultrasonic flaw detection (UT) is over 98%, while ensuring the quality of welding. The tire production schedule of the torsion box is guaranteed. The production process of the torsion box has been unanimously recognized by the shipowner and the ship inspection. It has been proved that the above process meets the welding quality requirements and can guide the actual production. The welding process of the torsion box thick plate has accumulated for the subsequent batch production of the thick plate. experience.
references:
[1] Zhao Weixing. Ship electric welder [M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2008.
About the author: Cai Jinyu, etc., assistant engineer of Shanghai Waigaoqiao Shipbuilding Co., Ltd.
Indoor Lighting,Home Ceiling Lighting,Led Flat Tube Batten Light,Indoor Led Linear Light
JIANGMEN MICHEN LIGHTING CO.,LTD , https://www.jmmission.com