Water rescue and lifesaving methods

Water rescue : It refers to the rescue measures taken by people in accidents when they are on water. It is an important measure to ensure the safety of swimmers. The water rescue work is a noble work of “rescuing and saving peopleâ€. Implementing the spirit of “giving priority to prevention, assisting salvation, combining prevention with rescue, and being prepared for everything.†A sound organization and emphasis on safety education to prevent swimming accidents are not only important for ensuring the safety of swimmers, but also for carrying out the “National Fitness Programâ€. "There's important meaning.
Application and operation of swimming lifesaving method
(1) Causes of flooding accidents and self-protection

1. Causes of drowning accidents 

(1) Technical factors
(2) Physiological and pathological factors
(3) Environmental factors
(4) Injury factors
(5) Lack of knowledge factor
(6) Psychological factors
(7) Organization and management factors
(1) Technical factors refer to not swimming or just learning to swim, but the mastery of the technique is still unfamiliar, and even the people are physically unable to support it, or are subject to human clashes and diving failures.
(2) Physiological and pathological factors refer to stagnation, satiety, hunger, drink and heart disease, hypertension, hypoglycemia, heat stroke, cramps, mental illness (including epilepsy), etc.
(3) Environmental factors 
Unfamiliar with the swimming environment leads to drowning
(4) Injury factors violate swimming pool regulations (dive, shallow water diving, etc.) causing drowning.
(5) Lack of knowledge factors such as: handling of cramps, drowning, rescue and other knowledge
6) Psychological reasons refer to fear of water and nervousness. When an accident occurs, panic, panic, and stiff limbs lead to drowning;
(7) Organizational management factors The swimming pool organization is not properly managed (the lifeguard is not equipped enough, the venue does not meet the requirements and other factors
(b) How lifeguards observe the water surface
"Observation", commonly known as "seeing water," that is, observing the status of the water surface, analyzing the nature of the accident, and judging first-aid measures are concrete manifestations of the "prevention-based" lifesaving work. It is the most important part of the entire lifesaving technique. The method is as follows: 
1. Life-saving personnel must be highly concentrative, glance (or look around) attentively and responsibly. It is necessary to divide the observation area by fixed and fixed points so that “emphasizing the key points (main responsibility area) and taking care of the entire area (cross observations, filling each other)â€.
2. The method of observation (when scanning the waters) must master the combination of "pool surface and pool bottom, pool surface and shore, point and surface".
3. When observing, it is necessary to look at the swimmers who are likely to drown on the surface of the pool and to see if there is any drowning under the water surface and at the bottom of the pool.
4. When sifting around the poolside waters, it is necessary to see whether there are any waterlogged seedlings in the poolside waters, but also whether there are unsupervised young children on the pool shore and swimmers who are pale, sitting and sitting on the shore.
5. When it is found that the technique is tough enough to follow the water, it is necessary to focus on tracking and observation, but it is not possible to stay awake and take care of the situation in order to prevent one from losing sight of others.
6. The division of the observation area (responsibility area) generally has a “straight line cutting methodâ€, that is, the swimming pool is roughly divided into several rectangular waters with straight lines (see Figure 6-14). "Arc cutting method" 
7. How the lifeguard judges the accident scene (taking a swimming pool as an example) 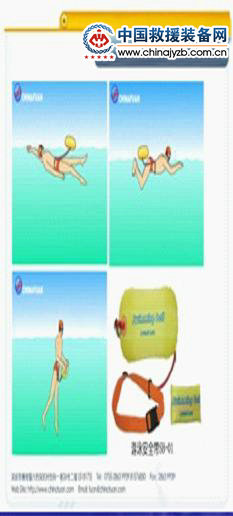
(1) Accidents at the beginning of the game: As swimmers have the eagerness to rush into the water, they will rush to the front with a ringing bell and they will rush to the next place. Most people will be chaotic afterwards, and they will easily overwhelm and overwhelm each other. The most prone to accidents.
(2) Accidents at the junction of depths and depths: At the junction of depths and depths, some seemingly innocent people are generally concentrated here. They are the “dangerous sections†in lifesaving.
(3) Accidents at the corner of the swimming pool in the deepwater area: Most swimmers in this area are swimmers who can swim a little. They often try their swimming skills in the diagonal of the swimming pool. Because they are basically unable to swim, Interfere with others, prone to accidents.
(4) Accidents in diving: In swimming pools that do not have diving functions, swimmers use running jumps, rebounds, and flips themselves to hit the wall of the pool and cause unconsciousness.
(5) Accidents in swimming discipline: If there is an accident such as snoring inside the pool, diving, splashing water, swimming in a direction other than the prescribed direction, alcohol abuse, etc.
(6) The swimmer's convulsions and loss of balance, disorganized movements, random intrusion, "no top" after a long period of time, and a snorkeling after lying on the bottom of the water or standing still in the water can all be considered as accidental alarms. 
(C) to save
1. Closer to the prostitute: Closer prostitutes are divided into indirect approach and direct approach.
(1) Indirect approach (also known as indirect rescue). The indirect rescue method is a technique in which lifeguards use life-saving equipment to rescue more awake ones. In general, swimming pools should be equipped with lifebuoys, bamboo rafts, planks, foam blocks, wheels, ropes and oxygen equipment. Here are some common lifesaving equipment and methods of use.
1 Lifebuoy:
It is a good idea to tie a rope around the lifebuoy, and when you find the leader, you can throw the lifebuoy to the leader. If you are in a river, throw it to the upper reaches of the leader. After getting the life preserver, the leader drags him to the shore.
2 Bamboo rafts: When the raft is close to the shore and the boat is near, you can use a bamboo raft to reach out to the raft and drag it to the shore or the boat.
3 Rope: Attach a float to one end of the rope and then throw the coiled rope in front of the leader so that the leader can hold the rope ashore.
4 Planks (including all floatables): In the absence of other life-saving equipment, planks can also be used as life-saving equipment. 
(2) Direct approach (also known as direct rescue)
The direct rescue method is a technique in which a lifeguard does not use any life-saving equipment to rescue the deaf person by hand. The direct rescue method is a technique in which a lifeguard does not use any life-saving equipment to rescue the deaf person by hand. Direct rescue techniques can be broadly divided into such processes as observation, entry into the water, swimming near the sea, underwater relaxation, towing, landing, and first aid on shore.
·1 Observation before water: When you find a person, immediately glance at the waters to determine the position of the deceased and its distance. In the rivers, lakes and seas, pay attention to the direction of the water flow, the width of the water surface, and the nature of the water bottom. The ambulancemen should follow the principle of swimming in the vicinity as soon as possible after entering the water, and quickly select the point of entry into the water.
2 into the water: refers to the rescuers in the discovery of drowning situation, by the shore (ship) diving to prepare for the rescue process. Enter the water quickly and pay attention to the goal. The main methods for entering water are:
a. Diving type (head first) b. Eighty type (step)
3 tours near the person:
After the rescuer enters the water, he or she quickly moves closer and controls the squadron to prepare for towing. In general, crawlers with higher speeds can be used, and breaststrokes that do not enter the water can be used to observe the deaf.
From 2-3 meters away from the scorpion, dive into the water and turn him back to himself, and then towing. 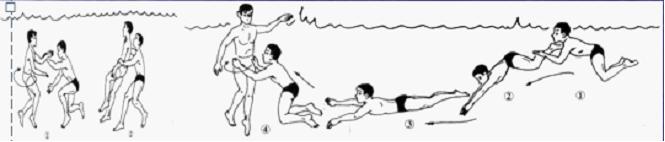
2. Water release method:
(1) Anti-scratch removal of tiger's mouth: (2) Elbow relief: 
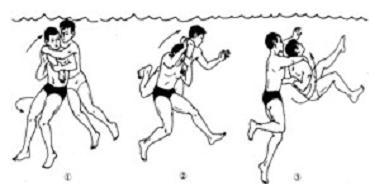
(3) Push torsion relief (1)
(4) Pulling finger withdrawal (2)
(5) External support release method (3)
3. Towing method: towing method refers to a lifeguard using side-bath or anti-breast swimming on the water transport a person's expertise.
(1) Side-swift towing method: 
(2) Anti-breastbanding: 
4. Ashore: 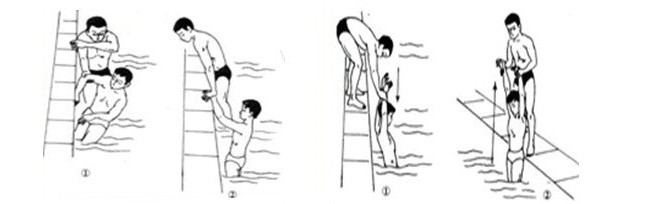
Shangqiu Jinda Tools Co.,Ltd , https://www.jindameasur.com