Lithium battery research made by the Chinese Academy of Sciences made a breakthrough in the world
Compared to the rapid development of the screen, processor performance technology, and flash memory chips, the lithium battery life is still the “top of Achilles†for electronic devices.

In terms of components, the lithium battery consists of a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, an electrolyte, etc. The key performance indicators (such as rate performance and cycle life) are determined by the electrochemical properties of the positive electrode material, among which LiFePO4 is a recognized positive electrode material.
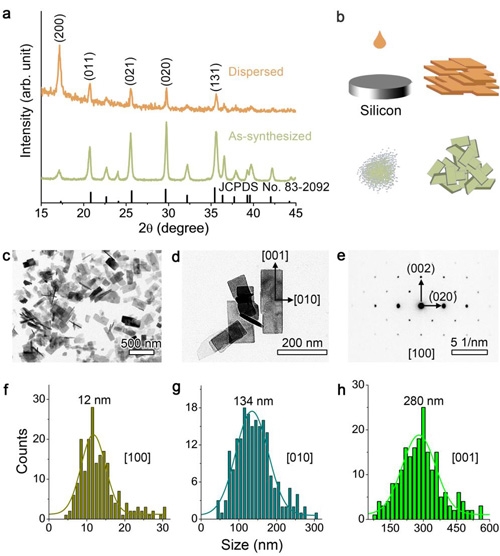
According to the report of the Institute of Metals of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the research team of the High Performance Ceramics Research Department of the Shenyang Materials Science National (Joint) Laboratory Wang Xiaohui's research group has prepared 12nm thick for the first time in the world by creating an extremely water-short acidic synthetic environment on the basis of previous research. The [100]-oriented LiFePO4 ultrathin nanosheets.
The significance of this nanosheet electrode lies in the smallest voltage gap so far, which increases the proportion of activated particles.
However, we know that the electrode is composed of a large number of particles, and its electrochemical performance mainly depends on the proportion of particles (activated particles) that participate in the electrochemical reaction during charge and discharge processes to the total number of particles.
According to the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the electrode has excellent rate performance and cycle life, and at 10C (60 minutes/10=6 minutes) charge and discharge rate, it can maintain 90% of the initial capacity after 1000 cycles. At 20C charge-discharge rate, the capacity can still reach 72% of the theoretical capacity.
It is generally believed that this research provides a new perspective and method for improving the capacity and life of lithium batteries and improving the life of electronic devices.

Thiocyanate (also known as rhodanide) is the anion [SCN]−. It is the conjugate base of thiocyanic acid. Common derivatives include the colourless salts Potassium Thiocyanate and Sodium Thiocyanate. Organic compounds containing the functional group SCN are also called thiocyanates. Mercury(II) thiocyanate was formerly used in pyrotechnics.
Thiocyanate is analogous to the cyanate ion, [OCN]−, wherein oxygen is replaced by sulfur. [SCN]− is one of the pseudohalides, due to the similarity of its reactions to that of halide ions. Thiocyanate used to be known as rhodanide (from a Greek word for rose) because of the red colour of its complexes with iron. Thiocyanate is produced by the reaction of elemental sulfur or thiosulfate with cyanide
Thiocyanate[4] is known to be an important part in the biosynthesis of hypothiocyanite by a lactoperoxidase.[5][6][7] Thus the complete absence of thiocyanate[8] or reduced thiocyanate[9] in the human body, (e.g., cystic fibrosis) is damaging to the human host defense system.[10][11]
Thiocyanate is a potent competitive inhibitor of the thyroid sodium-iodide symporter.[12] Iodine is an essential component of thyroxine. Since thiocyanates will decrease iodide transport into the thyroid follicular cell, they will decrease the amount of thyroxine produced by the thyroid gland. As such, foodstuffs containing thiocyanate are best avoided by Iodide deficient hypothyroid patients.[13]
In the early 20th century, thiocyanate was used in the treatment of hypertension, but it is no longer used because of associated toxicity.[14] Sodium nitroprusside, a metabolite of which is thiocyanate, is however still used for the treatment of a hypertensive emergency. Rhodanese catalyzes the reaction of sodium nitroprusside with thiosulfate to form the metabolite thiocyanate
Our main Thiocyanates are Sodium Thiocyanate, Potassium Thiocyanate, ammonium thiocyanate.
Thiocyanate
Sodium Thiocyanate, Potassium Thiocyanate,ammonium thiocyanate
SJZ Chenghui chemical co ltd , https://www.chenghuichemicals.com