The Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ) is one of the most critical aspects of welding metallurgy. It's the area of base metal that is not melted but has undergone significant changes in its microstructure due to exposure to high temperatures during welding. The HAZ can affect the mechanical properties of the metal, such as its hardness, toughness, and susceptibility to cracking. Controlling the HAZ is crucial in maintaining the integrity of the weld joint and the overall structure.
1. What is the Heat-Affected Zone (HAZ)?
The HAZ refers to the portion of the base material adjacent to the weld that has experienced thermal cycles (heating and cooling) intense enough to alter its microstructure, but not enough to melt it. While the weld pool itself forms the fusion zone (FZ), the HAZ surrounds this area and is divided into various temperature gradients, each affecting the material differently.
In many materials, especially carbon steels, stainless steels, and alloy steels, the HAZ is a critical factor in weld performance. The thermal history that the HAZ experiences during welding can induce hardness, brittleness, grain growth, and potential cracking if not carefully managed.
2. Metallurgical Changes in the HAZ
The changes that occur in the HAZ depend on several factors, including the material composition, the welding process, and the cooling rate. The HAZ can be broken down into three key subzones:
-
Coarse Grain Heat-Affected Zone (CGHAZ): Closest to the fusion zone, the CGHAZ experiences the highest temperatures just below the melting point of the base material. In steel, this causes grain growth and significant microstructural changes. Coarser grains result in reduced toughness, making the material more susceptible to cracking.
-
Fine Grain Heat-Affected Zone (FGHAZ): As you move away from the fusion zone, the metal experiences lower temperatures, leading to finer grain structures. Finer grains improve toughness and ductility compared to the coarse-grain zone.
-
Intercritical and Subcritical HAZ: These regions are farthest from the fusion zone and experience temperatures below the transformation point. The subcritical HAZ undergoes tempering, while the intercritical zone sees partial phase transformations. In steels, this area might include a mix of ferrite and pearlite or other phases, depending on the material.
In materials like aluminum alloys, the HAZ can cause precipitate dissolution and over-aging, reducing the material’s strength, which can be problematic in aerospace applications.
3. Effect of Welding Parameters on the HAZ
The extent and properties of the HAZ are highly dependent on the welding process parameters:
-
Heat Input: This is a critical factor influencing the size and properties of the HAZ. Heat input is determined by the welding process, current, voltage, and travel speed. A high heat input increases the size of the HAZ and can lead to grain coarsening and softening of the base metal in steels, increasing the risk of cracking.
Formula: Heat Input (kJ/mm) = (Voltage * Current * 60) / (1000 * Travel Speed)
-
Cooling Rate: The cooling rate after welding has a significant impact on the microstructural evolution of the HAZ. Rapid cooling in steels can lead to the formation of martensite, a hard but brittle phase, making the weld joint more prone to cracking. Controlled cooling, such as post-weld heat treatment (PWHT), can relieve residual stresses and temper martensitic structures, enhancing toughness.
-
Welding Technique: The use of multi-pass welding (especially in thicker materials) can alter the thermal cycles experienced by the HAZ, with subsequent passes reheating and tempering previously welded areas. This can improve the toughness of the HAZ.
4. Common Problems Associated with the HAZ
-
HAZ Cracking: Cracking in the HAZ is a common issue, especially in high-strength steels or thick sections. Hydrogen-induced cracking (HIC) or cold cracking often occurs due to the combination of a high hardness HAZ, residual stresses, and hydrogen absorption during welding.
-
Brittleness and Hardness: If the HAZ experiences too much grain coarsening or forms martensitic structures in steels, it can become excessively hard and brittle, increasing the risk of brittle fracture under stress.
-
Softening in Aluminum: In heat-treated aluminum alloys, such as 6061, the HAZ can experience precipitate dissolution, leading to softening. The strength of the aluminum alloy is significantly reduced in the HAZ compared to the parent material.
5. Controlling the HAZ
To ensure optimal weld performance and minimize problems in the HAZ, several control methods are used:
-
Preheating: Preheating the base material before welding helps reduce the cooling rate, minimizing the risk of HAZ hardening and cracking, especially in carbon steels. Preheating temperatures depend on the material but can range from 150°C to 300°C.
-
Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT): PWHT is a thermal process applied after welding to relieve residual stresses and improve toughness in the HAZ. In steels, PWHT reduces the hardness of martensite and improves ductility. The process typically involves heating the welded assembly to a temperature just below the transformation range and holding it for a specified time.
-
Low-Hydrogen Electrodes: Using low-hydrogen electrodes (such as E7018 for stick welding) or properly controlled shielding gases reduces hydrogen content in the weld, minimizing the risk of hydrogen-induced cracking in the HAZ.
-
Optimizing Heat Input: By using controlled heat input processes, such as pulsed MIG or TIG welding, welders can reduce the size of the HAZ and minimize grain growth. Pulsed techniques deliver high energy only during certain parts of the welding cycle, which controls the amount of heat absorbed by the base material.
6. Modern Techniques to Minimize HAZ Damage
Recent advancements in welding technology offer new ways to reduce the impact of the HAZ:
-
Laser Welding: Laser welding provides a highly focused heat source, minimizing heat input and significantly reducing the size of the HAZ. This technique is ideal for materials like stainless steel and titanium.
-
Electron Beam Welding: Like laser welding, electron beam welding delivers high energy density, reducing the HAZ and associated metallurgical changes.
Conclusion
The Heat-Affected Zone is a complex but critical aspect of welding that can significantly impact the performance of welded joints. Understanding how metallurgical changes in the HAZ occur and how to control them through process parameters, preheating, and post-weld treatments is essential for achieving strong, reliable welds. Proper control of the HAZ ensures longevity, reduces cracking risks, and optimizes the mechanical properties of the welded joint.
For more insights on welding techniques and advanced equipment, contact Quantum Machinery Group at Sales@WeldingTablesAndFixtures.com or call (704) 703-9400.
Reliable Pole Line Hardware Supplier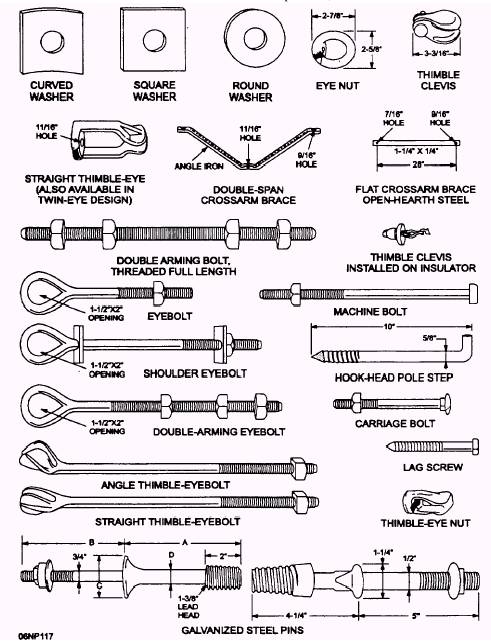
Pole line hardware refers to a range of products and accessories used in the construction and maintenance of overhead power lines. The poleline hardware includes various components such as pole brackets, crossarms, insulators, guy wires, and clamps that are essential for supporting and securing the electrical cables to utility poles.
These poleline hardware items are designed to withstand the weight and tension of the power lines, ensuring their safe and reliable operation.
Yokelink supply a full line of Poleline Hardware, we offer from the top of the pole to underground. Here are some of the pole line accessories that you are likely to use for your project:
Pole Bands
The pole band for poleline hardware is used as a point or platform for creating secondary racks to the utility pole. The pole band is sometimes referred t as a fastening clamp or simply a pole fastener.
Guy Wire
Also known as a stay wire, the guy wire for poleline hardware is usually used for enhancing the stability of the pole. The poleline guy wire balances the load that is on the electric pole.
Stay wire is usually assembled with other accessories such as pole bracket, guy thimble, and stay rod so that it can attach to the pole and ground. Guy wires for poleline hardware must have high tensional strength to sustain the forces against it.
Anchor Rods
You will have to buy poleline anchor rods whenever your project entails attaching guy wires onto the power line. The anchor rods plays the role of connecting the guy wire to the ground. The anchor rods for poleline hardware should be strong and have adequate tensile strength to support the force of the wire.
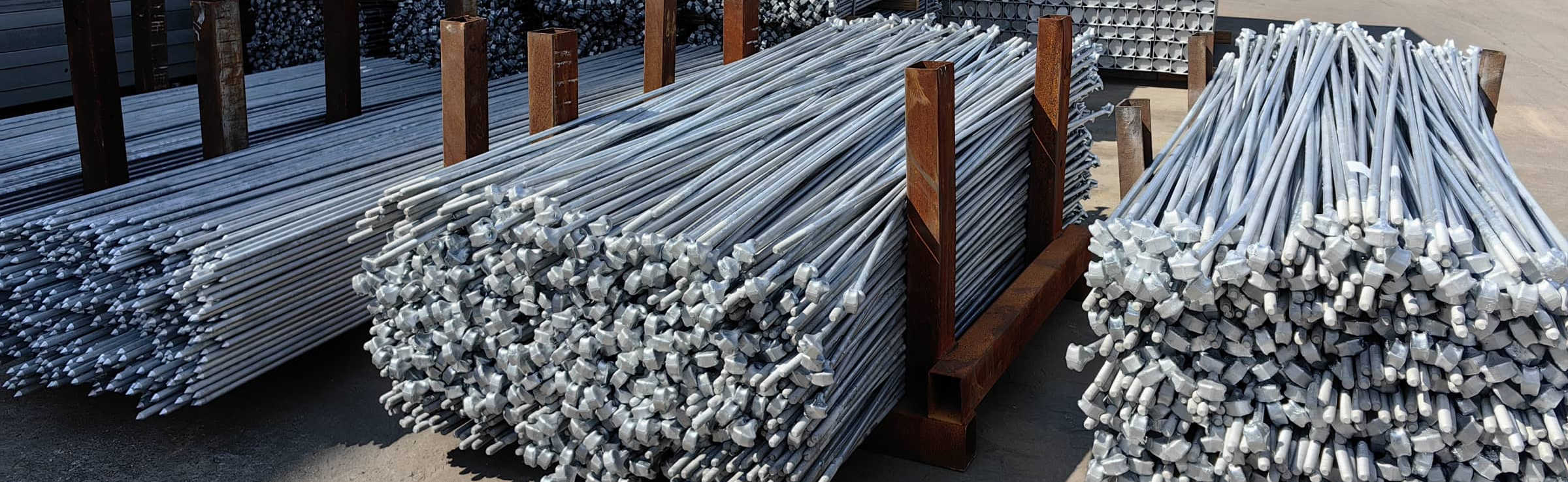

Hot dip galvanized Thimble anchor rods, ground rods.
Guy Clamps
The guy clamp for poleline hardware to secure the strands of guy wire. The poleline guy clamp comprises two pieces of carbon steel that are designed to form a parallel groove.The design of the guy clamp ensures that there is minimum damage caused on the strands of the guy wires.
Guy Grip
Also known as a dead-end guy grip, this pole line hardware is usually used on the distributed cables. The guy grip is usually attached to the grip conductor and as well as for the optical fiber.A guy grip has helical which is capable of holding the cable.
Guy Thimble

The guy thimble also know as cable thimble, this utility pole accessory is usually used in conjunction with guy grip. The guy thimble acts as an interface between the pole band and the guy grip. The guy thimble can also connect to the tension clamp in order to protect the ADSS cable. You can also use the guy thimble to connect the stay rod to the guy wire.
Insulator Clevis
A secondary insulator clevis comprises of a punched steel and a clevis pin. The insulator clevis for poleline hardware is also known as dead-end clevis and is characterized by the D-shaped bracket. The main function of this insulator clevis for powerline accessory is to connect with the pool insulator to the pole. Apart from the overhead line, the insulator clevis is also used on the dead end.
Crossarm Braces & Bracket
This utility poleline hardware is literally the arm of a streetlight pole. The corossarm bracket extends from the pole to provide a platform where you will attach the lighting fixtures. Streetlight arms come in different lengths and designs depending on the needs of the users.
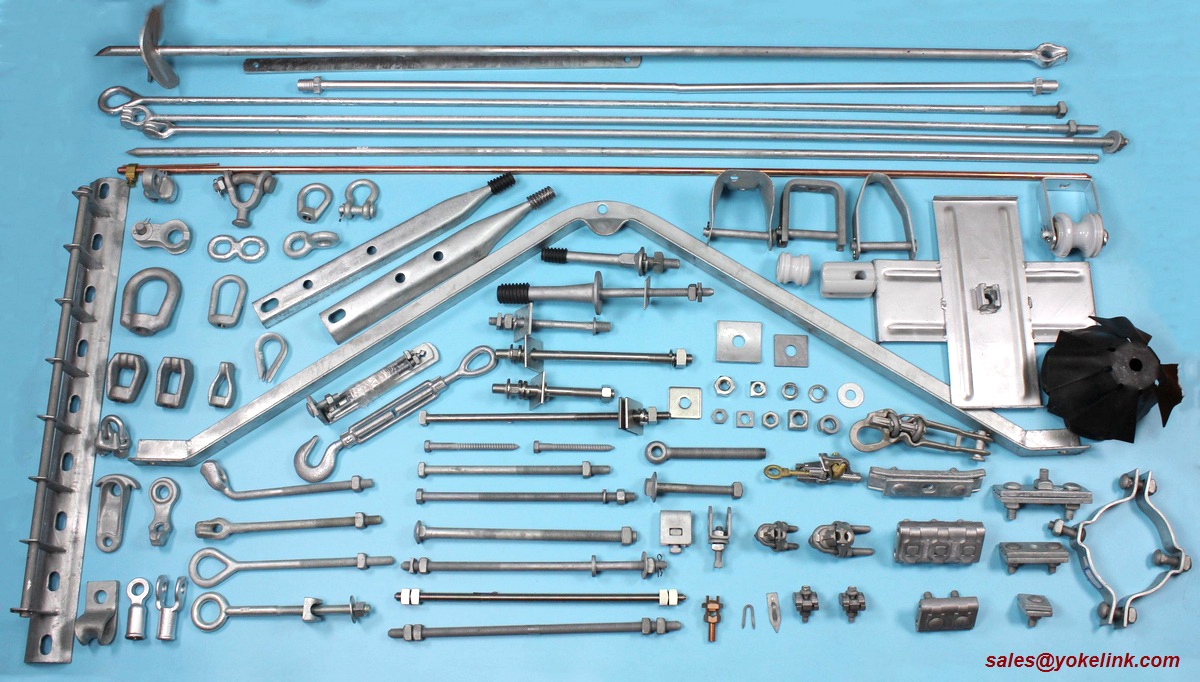
Yokelink Poleline Hardware
Yokelink have over than15 years of experience in stamping, Hot Forging, casting, Welding , and machining. Yokelink is a trusted manufacturer for power line hardware and electrical pole accessories. We supply a full line of Power line hardware, offer from the top of pole to the ground, leave your message, or send us an email. You can also call us to get answers to your questions and place your order.
Power line hardware, Utility pole hardware, Electrical pole hardware, Pole line construction hardware,Helical Anchors,Square Head Bolt,Forged Bolt,ANSI C135.1,Anchor Rods,ANSI C135.2,Hot Forging,forging,pole line construction,structures,Arrester Brackets
Ningbo Yokelink Machinery Co.,Limited , https://www.yokelink.com