Hefei Research Institute has made new progress in the simulation of liquid metal lithium lead corrosion
Recently, the Institute of Nuclear Energy Safety Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences Hefei Institute of Material Science has made new progress in the research of liquid metal lithium lead corrosion of structural steel. The research revealed the correlation between structural steel corrosion and crystal orientation. The relevant results were published in the International Journal of Nuclear Materials of Nuclear Materials.
The liquid metal cladding is one of the major international research projects on the fusion reactor cladding design. The design of fusion reactor cladding usually uses low-activated steel as the structural material, and the liquid metal lithium-lead alloy has the advantages of high working temperature, good thermal conductivity and high tritium proliferation ratio. The resistance of liquid lithium lead corrosion to structural materials such as low-activated steel is one of the key issues in the development of liquid metal cladding.
In response to this problem, the researchers carried out a simulation study on the corrosion of low-activated steel in the liquid metal lithium lead, and based on first-principles calculations revealed the correlation between corrosion and crystal orientation. At the contact surface of liquid lithium lead and low-activated steel, the liquid metal element arranged is preferably lead. Although the liquid metal elements occupy different adsorption sites on the (110), (001), and (111) surfaces, their coverage density at the contact surface is almost the same. In addition, calculations show that the corrosion of the low activation steel along the <110> crystal direction is more likely to occur than other crystal directions. The above research provides an important reference for the design of low-activated steel corrosion resistance.
The research was supported by the National Magnetic Confinement Fusion Energy Development Research Project and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
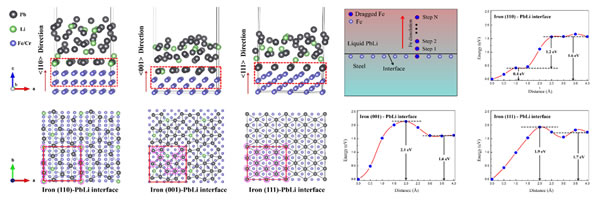
Structural steel / liquid metal lithium-lead interface structure (left) and the barriers to the migration of iron atoms from each crystal to the interface (right)
LED street lights are a modern and energy-efficient lighting solution for public spaces such as roads, highways, and parks. They use light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to produce bright and uniform light while consuming less energy than traditional street lights.
LED street lights are available in a range of wattages and luminous fluxes, allowing for customization to meet the specific lighting needs of different spaces. They also have a long lifespan, reducing maintenance costs and minimizing the need for frequent replacements.
In addition to their energy efficiency and durability, LED street lights offer other benefits such as instant-on lighting, dimming capabilities, and the ability to integrate with smart city technologies for improved management and control.
Overall, LED street lights are a reliable and sustainable lighting solution that can help cities and communities reduce their energy consumption and carbon footprint while providing safe and efficient lighting for public spaces.

LED street light housing,Streetlight Empty Housing,Outdoor Light Housing,Street Light Fixtures,Street Light Die Casting Housing
Yangzhou M.T. New Energy & Lighting Group Co., Ltd. , https://www.mtstreetlight.com